Blepharitis is a persistent and often bothersome eye condition that involves inflammation of the eyelids, specifically affecting the edges where the eyelashes grow. This common eye disorder can occur in people of all ages and backgrounds, causing discomfort and potentially leading to complications if not properly managed.
The condition manifests in various forms, from mild irritation to more severe symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the underlying causes, identifying symptoms, and exploring effective treatments are crucial steps in managing blepharitis and maintaining eye health.
Blepharitis can be categorized into different types, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches. The condition can result from bacterial or fungal infections, problems with oil gland function near the eyelashes, or even underlying skin conditions such as rosacea. These factors contribute to symptoms such as red, swollen eyelids, itching or burning sensations, crusting of the eyelashes (especially upon waking), and sensitivity to light.
Given its chronic nature, blepharitis requires ongoing management and care. Treatment strategies often involve a combination of eyelid hygiene practices, such as warm compresses and gentle cleansing, along with medications like antibiotics or anti-inflammatory agents. In more severe cases, advanced therapies such as steroid eye drops or procedures to unblock oil glands may be necessary.
Proper diagnosis and individualized treatment plans are essential for effectively managing blepharitis and minimizing its impact on eye comfort and health. Early intervention can prevent complications such as corneal damage or recurrent eye infections, ensuring optimal eye function and quality of life for those affected.
In this introduction, we delve into the complexities of blepharitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the spectrum of treatment options available to help individuals manage this common yet challenging eye condition.
Table of Contents
Types of Blepharitis

Blepharitis, characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, can manifest in different types, each with specific features and treatment approaches tailored to its underlying cause. Here are the primary types of blepharitis:
1. Anterior Blepharitis
- Description: Anterior blepharitis affects the outside front edge of the eyelid, where the eyelashes are attached. It often involves inflammation of the skin and hair follicles of the eyelashes.
- Causes: Common causes include bacteria (such as Staphylococcus aureus), seborrheic dermatitis (a type of skin condition), or allergies.
- Symptoms: Symptoms may include redness of the eyelid margins, crusty eyelashes (especially upon waking), itching or burning sensations, and sensitivity to light.
- Treatment: Treatment typically involves daily eyelid hygiene practices, such as warm compresses and gentle cleansing with baby shampoo or specific eyelid cleansers. Antibiotic ointments or topical corticosteroids may be prescribed in severe cases.
2. Posterior Blepharitis (Meibomian Gland Dysfunction)
- Description: Posterior blepharitis affects the inner edge of the eyelid where the Meibomian glands are located. These glands secrete oils that help lubricate the eye.
- Causes: Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) is a common cause, where the glands become blocked or dysfunctional, leading to inadequate oil secretion. This can result in tear film instability and dry eyes.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include red, swollen eyelids, irritation, a gritty sensation in the eyes, and excessive tearing or dry eyes.
- Treatment: Management focuses on improving Meibomian gland function through warm compresses, eyelid massages, and eyelid hygiene. Lubricating eye drops or ointments, oral antibiotics (such as doxycycline), or procedures like Meibomian gland expression may be recommended.
3. Mixed Blepharitis
- Description: Mixed blepharitis involves a combination of anterior and posterior forms, affecting both the outer and inner parts of the eyelids.
- Causes: This type may occur when factors contributing to anterior and posterior blepharitis are present concurrently.
- Symptoms: Symptoms can vary and may include a combination of those seen in both anterior and posterior blepharitis.
- Treatment: Treatment strategies typically address both aspects of the condition, incorporating measures to cleanse the eyelids, manage inflammation, and improve Meibomian gland function as needed.
4. Seborrheic Blepharitis
- Description: Seborrheic blepharitis is associated with seborrheic dermatitis, a skin condition characterized by oily, scaly patches on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body.
- Causes: It is often linked to overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia) on the skin, which leads to inflammation and flaking.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include greasy scales or flakes around the eyelashes, redness, and itching.
- Treatment: Treatment involves gentle cleaning of the eyelids with a mild cleanser or baby shampoo, and in some cases, antifungal medications or corticosteroid creams may be prescribed.
Understanding the type of blepharitis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. Effective management often requires a combination of eyelid hygiene practices, medications to reduce inflammation or manage infections, and addressing underlying factors such as dry eye or skin conditions. Consulting with an eye care professional can help tailor treatment to individual needs and ensure optimal eye health.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
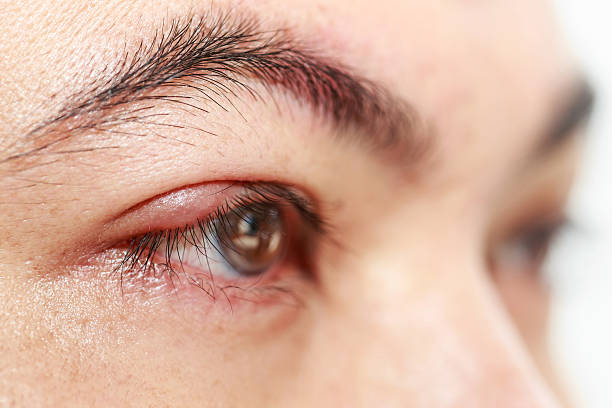
Symptoms of blepharitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Here are the common symptoms associated with blepharitis:
Common Symptoms of Blepharitis:
- Redness and Swelling of Eyelids:
- The edges of the eyelids may appear red and swollen, especially near the eyelash bases.
- Itching or Burning Sensation:
- Individuals with blepharitis often experience itching or a burning sensation along the eyelid margins.
- Crusty Eyelashes:
- Crusts or scales may form on the eyelashes, particularly upon waking in the morning.
- Greasy or Sticky Eyelids:
- The eyelids may feel greasy or sticky due to excess oil production or accumulation of debris.
- Tearing or Dry Eyes:
- Some people with blepharitis may experience excessive tearing (epiphora) or dry eyes, depending on the underlying cause (e.g., Meibomian gland dysfunction).
- Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia):
- Sensitivity to light can occur as a result of inflammation or irritation of the eyelids.
- Blurry Vision:
- In some cases, blepharitis may cause intermittent blurry vision due to tear film instability or ocular surface irregularities.
- Foreign Body Sensation:
- A sensation of having something in the eye (foreign body sensation) is common with blepharitis, often due to the presence of crusts or debris.
- Eyelash Loss or Misdirection:
- Chronic blepharitis can lead to eyelash loss or misdirection (trichiasis), where eyelashes grow inward toward the eye.
- Eye Irritation or Discomfort:
- Persistent irritation or discomfort in the eyes, exacerbated by blinking or rubbing, may be present.
Additional Symptoms Based on Type:
- Anterior Blepharitis:
- More noticeable crusts or scales around the eyelashes.
- Increased risk of staphylococcal infections causing recurrent styes or chalazia (localized eyelid bumps).
- Posterior Blepharitis (Meibomian Gland Dysfunction):
- Meibomian gland dysfunction-related symptoms such as Meibomianitis.
- Reduced oil secretion leading to dry eyes and tear film instability.
- Seborrheic Blepharitis:
- Oily, flaky scales around the eyelids, similar to dandruff.
- Associated with seborrheic dermatitis on other parts of the body.
Impact on Quality of Life:
Blepharitis symptoms can vary in intensity and may fluctuate over time. While typically not sight-threatening, untreated or poorly managed blepharitis can lead to complications such as chronic eye discomfort, corneal inflammation (keratitis), or even vision changes in severe cases.
It’s important to seek evaluation and guidance from an eye care professional if you experience persistent or bothersome symptoms of blepharitis. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate symptoms, improve eye comfort, and prevent potential complications associated with this chronic eye condition.
Causes of Blepharitis
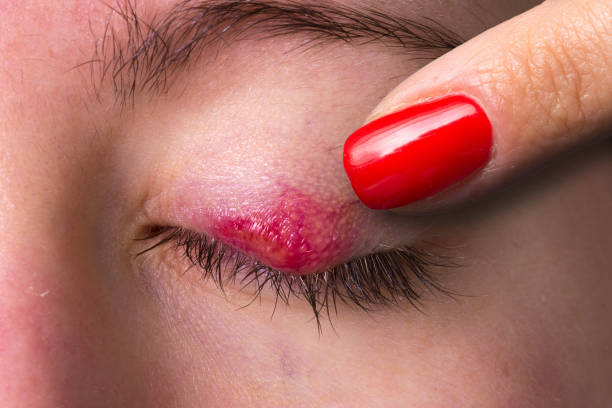
Blepharitis, an inflammation of the eyelids, can be caused by several factors, each contributing to different types and manifestations of the condition. Here are the primary causes and contributing factors of blepharitis:
1. Bacterial Infections
- Description: Bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus aureus, can colonize the eyelid margins and contribute to anterior blepharitis.
- Mechanism: These bacteria produce toxins that irritate the eyelid tissues, leading to inflammation and symptoms such as redness, swelling, and crusty eyelashes.
- Treatment: Antibacterial medications, such as topical antibiotics (e.g., erythromycin ointment), are commonly prescribed to manage bacterial blepharitis.
2. Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD)
- Description: Posterior blepharitis is often associated with dysfunction of the Meibomian glands, which are responsible for producing oils that lubricate the surface of the eye.
- Mechanism: When the Meibomian glands become blocked or inflamed (Meibomianitis), the quality and quantity of oil secretion are compromised. This can lead to tear film instability and dry eyes.
- Treatment: Management focuses on improving Meibomian gland function through warm compresses, eyelid hygiene, and sometimes oral antibiotics or procedures like Meibomian gland expression.
3. Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Description: Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by oily, scaly patches on the scalp, face, and other parts of the body.
- Mechanism: It can affect the eyelids, causing seborrheic blepharitis, which involves overgrowth of yeast (Malassezia) on the skin. This leads to inflammation and flaking of the eyelid skin.
- Treatment: Managing seborrheic blepharitis may involve gentle cleansing of the eyelids with mild baby shampoo or specific eyelid cleansers, along with antifungal treatments or corticosteroid creams as prescribed.
4. Allergic Reactions
- Description: Allergies to substances such as cosmetics, eye medications, or airborne allergens can trigger allergic blepharitis.
- Mechanism: The immune response to allergens can cause inflammation of the eyelids and exacerbate symptoms like itching, redness, and swelling.
- Treatment: Identifying and avoiding allergens, along with using allergy medications or topical antihistamines prescribed by a healthcare provider, can help manage allergic blepharitis.
5. Demodex Mites
- Description: Demodex mites are microscopic organisms that naturally inhabit the skin and hair follicles, including eyelash follicles.
- Mechanism: In some cases, an overgrowth of Demodex mites (Demodex infestation) can contribute to chronic inflammation of the eyelids, known as demodex blepharitis.
- Treatment: Treatment may involve eyelid scrubs with tea tree oil or other prescribed medications to reduce Demodex populations and alleviate symptoms.
6. Environmental Factors
- Description: Environmental factors such as air pollution, smoke, and dry or windy conditions can exacerbate symptoms of blepharitis.
- Mechanism: These factors can irritate the eyes and eyelids, contributing to inflammation and discomfort.
- Treatment: Minimizing exposure to irritants and maintaining good eyelid hygiene can help mitigate symptoms caused by environmental factors.
7. Systemic Conditions
- Description: Underlying systemic conditions such as rosacea, immune system disorders, or metabolic diseases can predispose individuals to blepharitis.
- Mechanism: These conditions may affect the immune response, skin health, or oil gland function, contributing to the development or exacerbation of blepharitis.
- Treatment: Managing the underlying systemic condition in consultation with a healthcare provider is crucial for effectively managing associated blepharitis symptoms.
Understanding the causes of blepharitis is essential for tailoring appropriate treatment strategies aimed at reducing inflammation, improving eyelid hygiene, and alleviating symptoms. Consulting with an eye care professional can help identify the specific type and underlying factors contributing to blepharitis and guide personalized management approaches for optimal eye health.
Diagnosis of Blepharitis
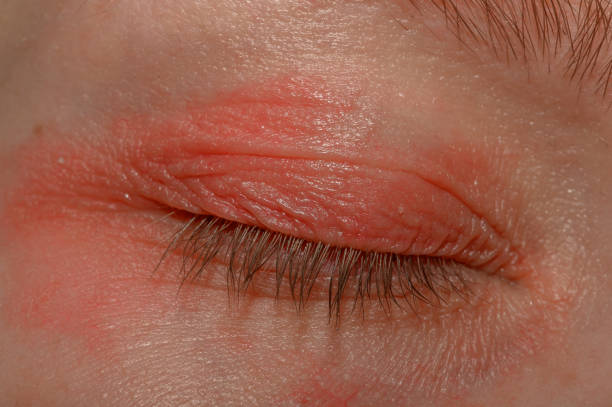
Diagnosing blepharitis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and sometimes additional tests to determine the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here’s how blepharitis is diagnosed:
1. Patient History
- Symptoms: The healthcare provider will inquire about symptoms such as eyelid redness, swelling, itching, burning sensations, crusting of the eyelashes, sensitivity to light, and any discomfort or changes in vision.
- Duration: They will ask about the duration and frequency of symptoms, including any factors that worsen or alleviate them.
- Medical History: They may inquire about any underlying health conditions (such as rosacea or allergies), previous eye infections, use of medications, and general eye care practices.
2. Clinical Examination
- Eyelid Examination: The healthcare provider will visually inspect the eyelids and eyelashes for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, crusting, or flaking.
- Meibomian Gland Assessment: For suspected posterior blepharitis or Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), the doctor may assess the Meibomian gland function by gently pressing on the eyelids to evaluate the quality and quantity of oil secretion.
3. Additional Tests and Procedures
- Eyelid Swab or Culture: In cases where bacterial or fungal infection is suspected, a sample may be taken from the eyelid for laboratory analysis to identify the specific pathogen causing the infection.
- Tear Film Evaluation: Assessment of tear film quality and stability may be conducted to evaluate for dry eye syndrome, which often coexists with blepharitis.
- Corneal Examination: In severe or chronic cases, a detailed examination of the cornea may be performed to check for signs of corneal inflammation (keratitis) or other complications.
4. Differentiating Types of Blepharitis
- Based on the clinical presentation and findings, the healthcare provider will differentiate between anterior blepharitis (involving the eyelid margin and eyelashes) and posterior blepharitis (involving the Meibomian glands).
5. Underlying Conditions
- If there are indications of underlying systemic conditions such as rosacea or allergies, further evaluation or referral to a specialist may be recommended to manage these conditions in conjunction with blepharitis.
6. Comprehensive Evaluation
- A comprehensive evaluation helps in determining the appropriate treatment approach, which may include eyelid hygiene practices, medications (such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory agents), management of underlying conditions, and lifestyle modifications.
7. Follow-Up
- Regular follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor the response to treatment, adjust management strategies as needed, and prevent recurrence or complications associated with blepharitis.
Diagnosing blepharitis involves a thorough assessment of symptoms, clinical examination of the eyelids, and sometimes additional tests to identify underlying causes. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential for reducing symptoms, improving eye comfort, and preventing long-term complications. Seeking guidance from an eye care professional ensures personalized care and effective treatment tailored to individual needs.
Treatments for Blepharitis
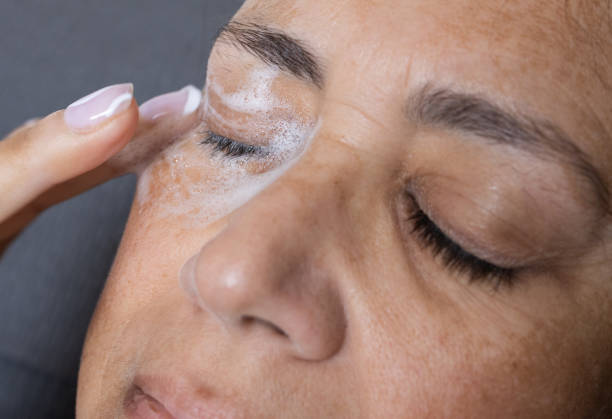

Treatment for blepharitis aims to reduce inflammation, improve eyelid hygiene, manage underlying causes, and alleviate symptoms. The approach may vary depending on the type and severity of blepharitis. Here are common treatments and management strategies:
1. Eyelid Hygiene
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the closed eyelids for 5-10 minutes can help loosen crusts, open blocked Meibomian glands, and reduce inflammation.
- Eyelid Scrubs: Using a clean washcloth, cotton swab, or commercial eyelid cleanser (such as Ocusoft or Sterilid) to gently cleanse the eyelid margins can remove debris and bacteria.
- Lid Massage: Gentle massage of the eyelid margins after warm compresses can help express oils from Meibomian glands and improve tear film quality.
2. Medications
- Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotic ointments (e.g., erythromycin or bacitracin) or antibiotic eye drops may be prescribed for anterior blepharitis to manage bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
- Topical Corticosteroids: In severe cases or for short-term use, corticosteroid eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms.
- Oral Antibiotics: For posterior blepharitis or Meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD), oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or azithromycin may be prescribed to manage bacterial overgrowth and improve Meibomian gland function.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Prescription medications like cyclosporine (Restasis) or lifitegrast (Xiidra) may be used to reduce inflammation and improve tear production in cases associated with dry eye syndrome.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
- Avoidance of Irritants: Minimizing exposure to environmental irritants, such as smoke, dust, or allergens, can help reduce inflammation and symptoms.
- Cosmetic Considerations: Avoiding eye makeup, especially during flare-ups, and ensuring all makeup tools are clean can prevent exacerbation of blepharitis.
4. Management of Underlying Conditions
- Treatment of Associated Conditions: Managing underlying conditions such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis with appropriate medications and skincare regimens can help control blepharitis symptoms.
5. Advanced Therapies
- Meibomian Gland Expression: This procedure involves manually expressing blocked Meibomian glands to improve oil flow and relieve symptoms of Meibomian gland dysfunction.
- LipiFlow: A device that applies heat and pressure to the eyelids to improve Meibomian gland function and alleviate symptoms of MGD.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: IPL therapy has shown effectiveness in reducing inflammation and improving Meibomian gland function in cases of refractory blepharitis.
6. Regular Follow-Up and Maintenance
- Monitoring: Regular follow-up visits with an eye care professional are essential to monitor treatment effectiveness, adjust therapies as needed, and prevent recurrence or complications.
- Long-Term Management: Blepharitis is often chronic, so maintaining good eyelid hygiene practices and managing contributing factors can help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
7. Educational Resources
- Patient Education: Providing education on eyelid hygiene techniques, the importance of compliance with treatment regimens, and lifestyle modifications can empower patients to manage blepharitis effectively.
Treatment for blepharitis is often tailored to individual needs based on the specific type and severity of the condition. Consulting with an eye care professional ensures personalized care and comprehensive management strategies to alleviate symptoms and optimize eye health.
Potential Complications
Blepharitis, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to several potential complications affecting both eye health and overall well-being. Here are some of the potential complications associated with blepharitis:
1. Chronic Eye Discomfort and Irritation
- Persistent inflammation of the eyelids can cause chronic discomfort, irritation, and sensitivity to light (photophobia), affecting daily activities and quality of life.
2. Dry Eye Syndrome
- Blepharitis often coexists with dry eye syndrome, where inadequate tear production or poor tear quality leads to dryness, burning sensations, and a gritty feeling in the eyes.
3. Corneal Issues
- In severe cases or when blepharitis is chronic, inflammation of the eyelids can compromise the health of the cornea (the transparent front part of the eye). Potential complications include:
- Corneal Erosion: Persistent inflammation and mechanical irritation from eyelid abnormalities or debris can lead to corneal erosions.
- Corneal Ulcers: Infections or abrasions on the cornea can develop, particularly if bacteria from the eyelids invade the corneal tissue.
- Corneal Scarring: Chronic inflammation and repeated episodes of irritation can cause scarring of the cornea, potentially affecting vision.
4. Eyelid Structural Changes
- Long-standing blepharitis can lead to structural changes in the eyelids, such as:
- Trichiasis: Misdirection of eyelashes toward the eye, causing them to rub against the cornea and irritate the surface.
- Eyelid Margin Irregularities: Thickening or distortion of the eyelid margins, impacting tear distribution and exacerbating dry eye symptoms.
5. Recurrent Styes or Chalazia
- Bacterial involvement in anterior blepharitis can predispose individuals to recurrent styes (external hordeolum) or chalazia (internal hordeolum), which are painful eyelid bumps caused by blocked oil glands.
6. Psychosocial Impact
- Chronic eye discomfort and visible symptoms (e.g., red, swollen eyelids) can affect self-esteem and social interactions, particularly if blepharitis leads to persistent eye rubbing or avoidance of eye contact.
7. Impact on Vision
- Severe complications such as corneal ulcers or scarring can potentially affect vision, highlighting the importance of prompt diagnosis and effective management of blepharitis to prevent long-term visual impairment.
8. Systemic Associations
- Certain types of blepharitis, such as those associated with rosacea or other systemic conditions, may indicate broader health concerns that require comprehensive management and monitoring.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
- Early Intervention: Prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and reduce the severity of blepharitis symptoms.
- Regular Eye Exams: Routine eye exams with an eye care professional can help monitor eye health, identify early signs of blepharitis, and adjust treatment as needed.
- Comprehensive Care: Managing underlying conditions (e.g., rosacea, dry eye syndrome) and maintaining good eyelid hygiene practices are crucial for preventing complications and optimizing eye health.
Understanding the potential complications associated with blepharitis underscores the importance of proactive management and regular follow-up with healthcare providers. By addressing symptoms promptly and implementing effective treatment strategies, individuals can minimize the impact of blepharitis on their eye health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blepharitis is a common yet challenging condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, which can lead to a range of symptoms and potential complications if not effectively managed. Understanding the underlying causes, such as bacterial infections, Meibomian gland dysfunction, or systemic conditions like rosacea, is crucial for tailoring appropriate treatment strategies.
Effective management of blepharitis involves a combination of eyelid hygiene practices, medications to reduce inflammation and manage infections, and addressing any underlying systemic conditions. Early intervention can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications such as corneal damage or chronic dry eye syndrome, and improve overall eye comfort and quality of life.
Regular follow-up with an eye care professional is essential to monitor treatment progress, adjust therapies as needed, and prevent recurrence of blepharitis. By maintaining good eyelid hygiene, avoiding potential triggers, and seeking prompt medical attention for persistent or worsening symptoms, individuals can effectively manage blepharitis and minimize its impact on eye health.
Overall, proactive management and comprehensive care are key to managing blepharitis successfully, ensuring optimal eye health and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by this chronic eye condition.
